© AGFW
© AGFW
Integration of volatile renewable energies
Condition assessment of heating networks with volatile operating modes
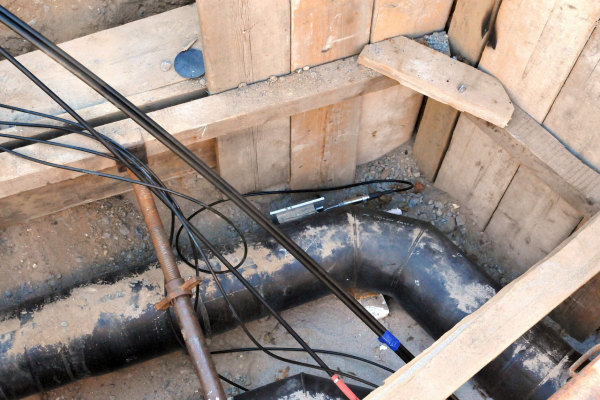
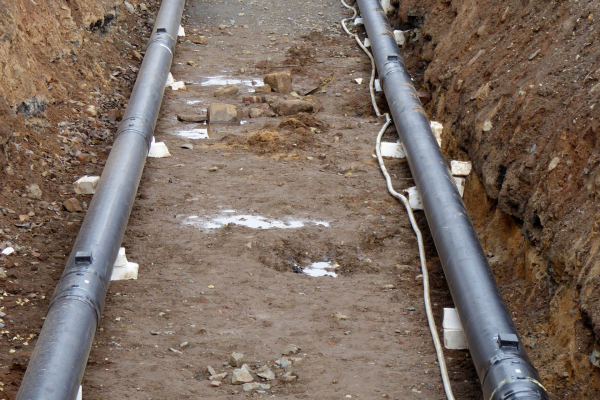
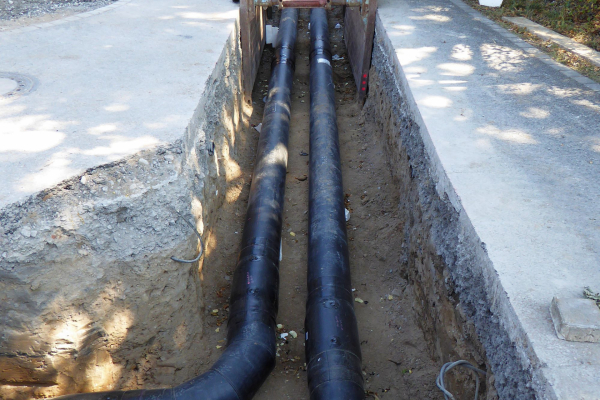
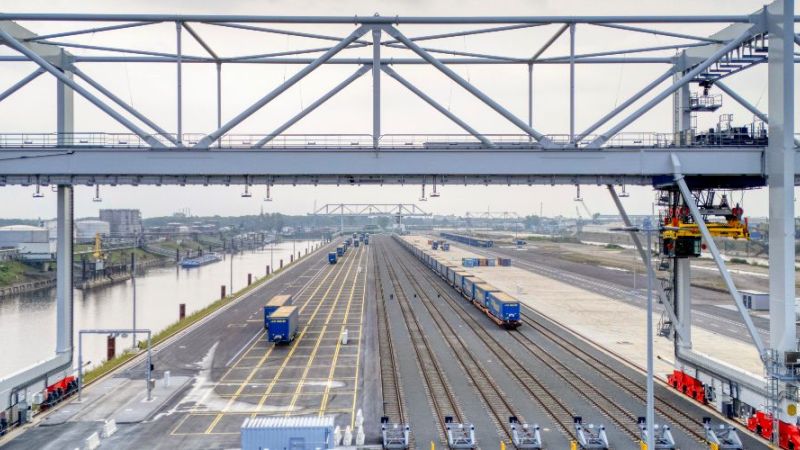
The integration of volatile, renewable heat sources in district heating networks leads to an increase in temperature changes and thus to a greater load on the materials. The research project is aiming to develop transferable condition assessments of district heating networks. To this end, the researchers are recording their actual loads based on operating data from utility companies and long-term monitoring results. This will enable the material characteristics of the system components to be determined more precisely for planning and designing line sections and entire networks. The project results will be incorporated into concepts that will extend the useful service life of the networks.
The integration of renewable energy into Germany's energy system poses a challenge to district heating networks to a previously unparalleled extent. CHP power plants require a flexible mode of operation to enable them to respond to volatile renewable power generation. At the same time, volatile renewable heat sources will have to be increasingly integrated directly into district heating systems in the long term. For the district heating networks this means an increase in the temperature changes and thus an increase in the loads on the materials, resulting in a shortening of the service life. The influence of increased cycle loads on the networks is unknown. These arise in particular
- through the flexibilisation of the power plant fleet through storage systems,
- through the use of the network as a storage system,
- with volatile solar thermal feed-in,
- through the flexible operation of CHP plants and the temporary shutdown of power blocks and
- with an increase in the connection density through expanding the district heating in smaller line sections.
The project is investigating the effects of real-case cyclic loading on heating networks. The findings will help to qualify heating networks for future challenges and also identify load limits in order to achieve a high level of supply security with increasing volatile heat generation.
The tasks of the research partners are defined by six work packages. In Work Package 1, the real loads, future modes of operation and economic influence parameters will be determined. In Work Packages 2 to 5, qualified test institutes and research facilities will conduct material investigations and develop system components for the mechanical replacement model. These will be brought together in Work Package 6, tested by means of sample calculations and prepared for the relevant standardisation committees.
 © AGFW
© AGFW
Forschungsfokus
Ausgangspunkt der Untersuchungen war die Ermittlung realer Beanspruchungen erdverlegter Kunststoffmantelrohre (KMR) anhand von In Situ Langzeitmessstellen in Wärmenetzen. Hierbei wurde angenommen, dass insbesondere die temperaturbedingten Wechselbeanspruchungen, die durch die Fahrweisen der Erzeugungsanlagen entstehen, die Gebrauchsdauer von Trassenabschnitten eines Netzes bestimmen. Durch Materialuntersuchungen werden die Belastungsgrenzen von Systemkomponenten wie Polyurethan-Hartschaum, PE-HD Mantel, Dehnpolster sowie umliegendes Erdreich und Mantelrohrverbindungen bestimmt. Dabei handelt es sich um eine komplexe Beanspruchung durch beispielsweise Temperatur, mechanische Wechselbeanspruchungen oder Feuchte. Mit den Ergebnissen der Materialuntersuchungen wurde das bestehende mechanische Modell für den Ersatz von Systemkomponenten erweitert. Zusätzlich erarbeiteten die Forschenden eine Methodik zur Zustandsbewertung von Leitungsabschnitten anhand von Temperaturfahrweisen. Die Erkenntnisse fließen in neue ingenieurtechnische Werkzeuge zur Integration erneuerbarer Energien in bestehende Wärmenetze ein.
 © AGFW
© AGFW
Zentrale Idee und Ansatz
Der Stand des Wissens über lebensdauerlimitierende Faktoren eines Fernwärmesystems bildet den Ausgangspunkt des Projekts. Denn Materialkennwerte seiner Systembausteine bei zyklischen, überlagerten Belastungen wurden bislang noch nicht untersucht. Mit den Forschungsergebnissen sollen reale Belastungszustände abgebildet und technische Zustände bestehender Netze besser abgeschätzt werden. Dies ermöglicht eine optimierte Erzeugung der benötigten Wärmemengen und einen schonenderen Umgang mit der Ressource Fernwärmenetz. Darüber hinaus bilden die Projektergebnisse eine notwendige Grundlage für die künftige technische Qualifikation von Fernwärmenetzen. Die Migration der Projektergebnisse in die Branche und entsprechende Normen wird durch einen projektbegleitenden Arbeitskreis, dem Versorgungsunternehmen, Rohrhersteller, Ingenieurbüros und Forschungsstellen angehören, sichergestellt.
Erprobung und Anwendung
Die Erkenntnisse aus dem Forschungsvorhaben wurden in zahlreichen Publikationen zusammengefasst.