Geothermal Energy
Great need for research on geothermal energy
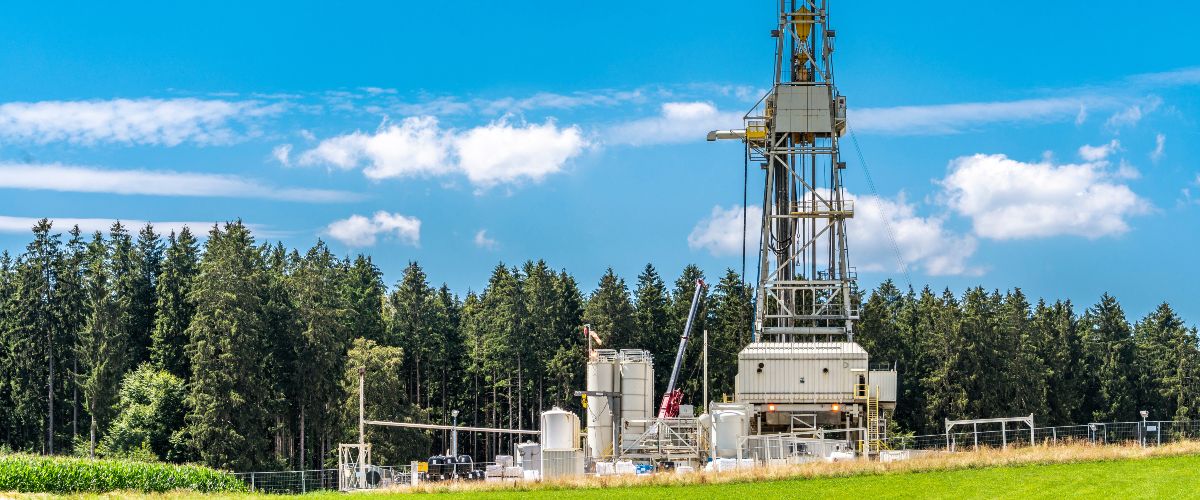
Geothermal energy is a key technology for the energy and heating transition. It is reliably available all year round and can make a significant contribution to the decarbonisation of the heat supply. Regardless of the depth (near-surface, medium-deep, deep), geothermal energy can provide sustainable and resilient heating and cooling for existing buildings, new buildings and industrial processes.
The huge potential for a climate-neutral heat supply has not yet been sufficiently tapped. Upscaling geothermal energy has a significant impact on the cost price of thermal energy. Furthermore, cross-sectoral system integration and the system usefulness of geothermal energy play an important role.
Research content eligible for funding in geothermal energy
Projects that help to make the utilisation of geothermal energy more efficient, cost-effective or reliable are eligible for funding. This includes the new and further development of geothermal-specific exploration methods as well as tools and processes with the aim of reducing drilling and completion costs. Furthermore the BMWK funds research on the optimisation of materials and components, in particular pumps, filters and pipes that meet typical geothermal conditions, and measuring and monitoring systems. In addition, projects on minimising induced seismic activity, processes to protect against mineral precipitation and corrosion, the use of geothermal probes and large heat pumps to provide heat in line with demand are eligible for funding. The ministry also supports research on stimulation processes to develop and optimise geothermal reservoirs as well as innovative development concepts, sustainable reservoir management and the development of new sites for geothermal plants. Non-technical innovations and aspects of social acceptance are also eligible for funding, provided they are linked to applied technological development projects.
In addition to the technical issues of heat supply, other key aspects include issues relating to the economic operation of geothermal heat generation and storage as well as integration into building supply, regional heating concepts, and conversion of existing conventional district heating networks as well as the development of the necessary components, processes and interfaces. Research and development activities on geothermal energy are therefore particularly linked to the funding areas of buildings and neighbourhoods as well as heating networks and heat storage. In addition, geothermal heat supply and storage for process heat in industry, for example in combination with other heat sources and heat pumps, is another area of research.
Other relevant geothermal research topics
Besides generation, the storage of heat plays a central role in the systemic integration, flexibilisation and stabilisation of the energy system. Underground storage is therefore addressed as both seasonal and situational storage. Coupling with other renewable heat sources and concepts for system-beneficial utilisation and sector coupling are being sought. In addition to the above-mentioned research topics, the BMWK's research funding programme includes the expansion of possible applications for geothermal energy and thus the preparation of new business areas. This includes the combination with innovative technologies, for example new types of heat pumps, in order to achieve high process temperatures, for example.
The funding is not limited to innovations in geothermal plants and the corresponding peripherals. The funds made available will also be used to make geothermal energy utilisation in Germany and, where applicable, in export markets more predictable and safer overall through additional empirical knowledge. For this reason, innovations are also supported with regard to the availability of geological data, risk minimisation, digitalisation and automation as well as digital planning, optimisation and control tools. Aspects of long-term environmental compatibility and soil and groundwater protection are also important.